A study on power improvement emission characteristics of marine diesel engine with response power 220HP turbocharger
This is a thesis about the experiment of comparison characteristic of power and exhaust gas in the same condition between diesel engine that is equipped response power 220HP turbocharger to increase effectiveness of the engine which is recently used in a lot of industry which requires high power. Resulting of the experiment with natural aspiration diesel engine and turbocharger diesel engine, difference in low speed is not significant, but in high speed, effectiveness of turbocharger diesel engine is much higher than the other one. In other hand, in exhaust gas experiment, turbocharger model exhausts more NOX and O2, but it doesn’t significantly affect the result when it comes with decreasing of CO2 and effectiveness of increased power characteristic. As a result, the turbocharger diesel engine is economically effective comparing with the natural aspiration diesel engine.
초록
최근 높은 출력을 요구하는 각종 산업분야에서 사용되고 있는 디젤엔진의 효율을 높이기 위해 대응출력 220HP 과급기를 장착한 디젤엔진과 자연흡기식 디젤엔진을 동일한 조건에서 동력계와 배출가스 분석기를 통해 동력특성 및 배출가스 특성을 실험한 논문이다. 자연흡기식 디젤엔진과 과급기를 장착한 디젤엔진을 실험한 결과, 저속에서의 동력특성의 차이는 적었으나 고속에서의 동력특성은 과급기를 장착한 엔진의 출력과 효율이 증가한다는 결과를 얻을 수 있다. 이와는 반대로 배출가스 특성에서는 과급기를 장착한 모델에서 NOX와 O2등의 배출가스가 증가되었으나 CO2의 저감과 동력 특성 증가의 효율을 볼 때 배출가스의 증가치는 적다고 할 수 있다. 이와 같은 결과를 토대로 과급기가 장착된 디젤엔진이 자연흡기식 엔진 대비 효율성 면에서 경제성이 높다라고 예측된다.
Keywords:
220hp class Turbocharger, Exhaust Gas, Engine Performance, Marine Diesel Engine, 220마력급 과급기, 출력향상, 선박용 디젤 엔진1. 서 론
자동차는 문명의 발달에 따라 이제는 우리 생활과 뗄 수 없는 밀접한 관계를 유지하고 있다. 그러나 자동차의 증가에 따라 자동차에서 배출되는 유해 가스에 의한 환경오염과 인체에 미치는 영향에 대한 우려도 커지고 있다. 이에 따라 자동차의 배기가스를 줄이기 위한 저공해 내연기관에 대한 연구가 계속 이루어져 왔다[1].
디젤엔진은 가솔린엔진보다 연료효율이 높고 일산화탄소와 탄화수소의 배출량이 적지만 진동과 소음이 크고 질소산화물과 미세먼지의 발생량이 높아 대기오염을 악화시킨다는 우려 때문에 상용차에는 적용되어 왔지만 승용차에 탑재하는 과정에는 여러 가지 어려움이 많았다. 특히, 19080년대 후반부터 개발된 연료 직접분사장치와 과급장치 기술의 개발로 출력, 소음, 진동 등 성능이 크게 향상되었으며, 최근에 개발되어 상용화된 고압연료분사장치인 커먼레일 시스템, 배기가스 재순환장치, 디젤 미립자 여과장치, 촉매 변환장치의 적용으로 배기가스를 물리적, 화학적으로 정화하는 기술이 크게 발전하여 유럽을 중심으로 승용차에 디젤엔진의 탑재가 시작되었다[2]. 최근에는 소형 선박에 장착된 디젤엔진에 과급기를 통한 과급 기술을 적용하여 환경 오염대책에 대응하고 있다[3]. 본 연구에서는 소형 선박디젤엔진에 적용되고 있는 디젤엔진을 활용한 자연흡기식(이하 N/A) 디젤엔진과 대응출력 220마력 과급기(이하 T/C)가 장착된 디젤엔진을 비교 실험하며, 기관의 운전 조건으로는 부하와 회전수를 선정하고 이 운전 조건에 따른 동력 성능 및 배출특성을 파악하여 디젤엔진의 고출력화 및 배출가스 저감을 위한 기초자료로 활용하고자 한다.
2. 실험장치 및 방법
2.1 실험장치
실험에 사용된 시험장치는 동력계(700HP급), 동력계 제어 시스템, 조절판 컨트롤 시스템, 청수 온도제어 시스템, 연료 소모량 측정기로 구성하였고, 동력계의 제원은 Table 3과 같고, Figure 3은 연료 소모량 측정기, Figure 4는 배출가스 분석기(Horiba MEXA-7100DEGR)을 사용하여 배출가스를 측정하였다.
2.2 실험방법
자연흡기식 디젤엔진과 과급기가 장착된 디젤기관에서의 동력성능 및 배출특성을 비교 측정하는 실험이므로 기관 운전 조건인 부하와 회전수를 제어하여 실험을 실시하였다. 실험은 KS B 6002의 규정에 따라 소형 육용 내연기관 성능 시험방법 중 부하 운전시험을 채택하여 진행하였다[4][5].
엔진의 회전수는 1,000RPM, 1,500RPM, 2,000RPM으로 고정하고, 조절변은 부하 운전시험인 점을 고려하여 실주행 조건과 같은 운전 조건을 만들기 위해, 각 RPM에 따라 1,000RPM에서는 0%에서 1분당 5%씩 60%까지 개방한 결과 값을 측정하였고, 1,500RPM에서는 70%까지 2,000RPM에서는 80%까지 측정하였다. 조절판 밸브가 5% 열릴 때마다 10초 간격으로 측정하고, 조절변의 안정화를 위하여 10초 이후부터 1분당 5개 측정값을 측정하였다.
모든 실험을 동일한 조건에서 2회씩 실시하였고, 그 평균값을 결과의 값으로 하였다. 실험에서 얻어진 데이터를 기반으로 하여 동력성능 및 배출가스 측정결과는 다음과 같이 나타났다.
3. 실험결과 및 고찰
3.1 동력성능
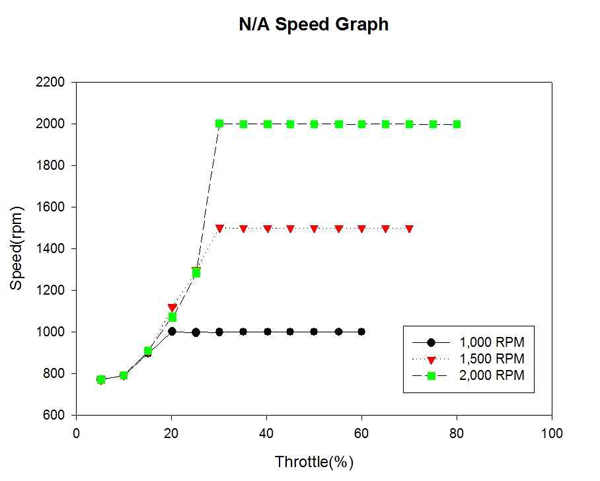
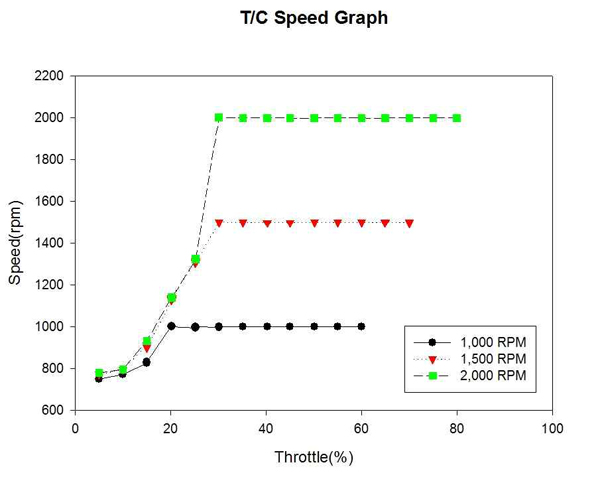
Figure 5는 자연흡기식 엔진의 각 고정 회전수까지의 엔진 회전수 변화를 계측하여 비교한 것이다. Figure 6은 대응출력 220HP 과급기 장착에 따른 엔진의 각 고정 회전수까지의 엔진 회전수 변화를 계측하여 비교한 것이다. 일반적인 터보기관에서 발생하는 터보랙 구간이 나타나지 않은 것은 엔진의 배기량에 비해 터빈 용량이 적어 풍부한 풍량이 계속해서 터빈에 공급되었기 때문이라 예측된다.
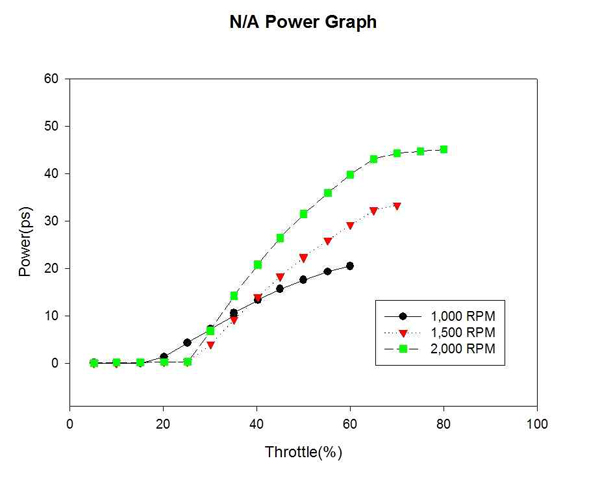
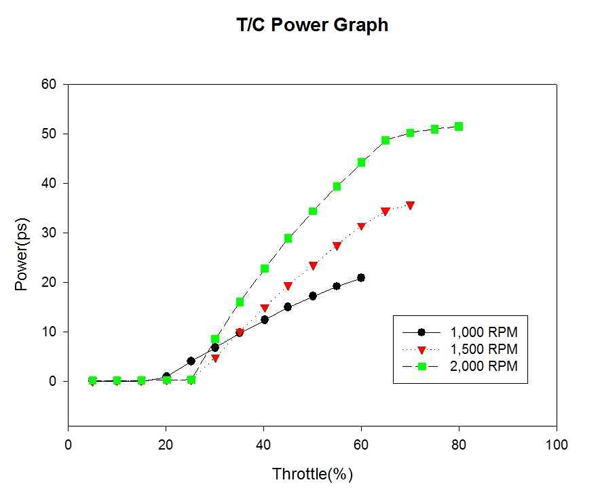
Figure 7은 자연흡기식 엔진의 각 고정 회전수까지의 엔진 동력 변화를 계측하여 비교한 것이다. Figure 8은 대응출력 220HP 과급기 장착에 따른 엔진의 각 고정 회전수까지의 엔진 동력 변화를 계측하여 비교한 것이다. 엔진의 동력은 저속구간에서는 큰 차이를 보이지 않았으나 고속구간에서는 T/C 엔진의 동력이 13% 가량 증가하였다. 이는 일반적인 T/C 엔진의 동력 효율이라 예측된다.
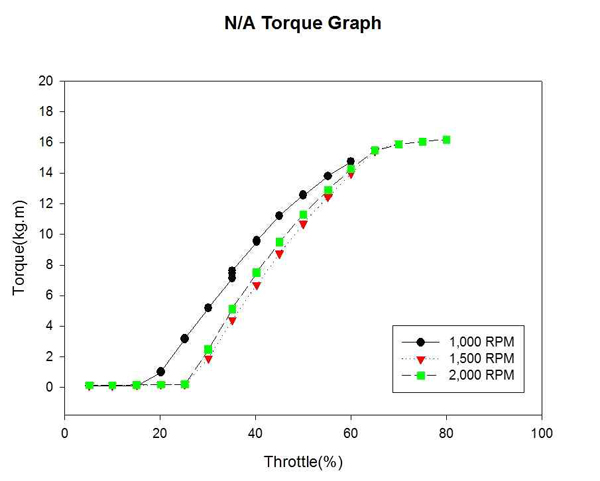
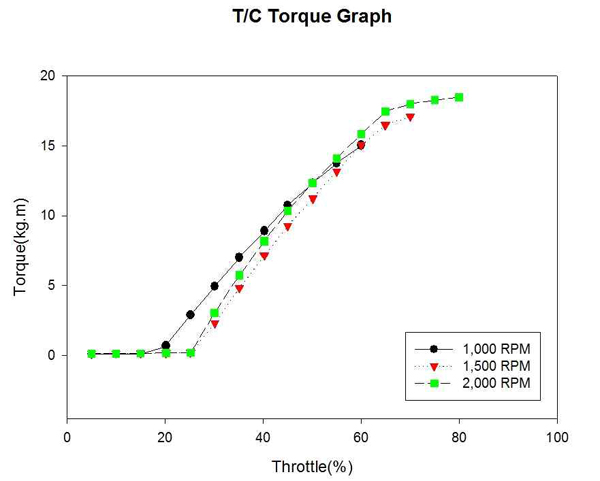
Figure 9는 자연흡기식 엔진의 각 고정 회전수까지의 엔진 회전력 변화를 계측하여 비교한 것이다. Figure 10은 대응출력 220HP 과급기 장착에 따른 엔진의 각 고정 회전수까지의 엔진 회전력 변화를 계측하여 비교한 것이다. 엔진의 동력과 마찬가지로 회전력도 고속구간에서 증가하였으며, 이는 동력과 회전수의 관계에 의해 회전력 또한 비례하여 증가한 것이라 예측된다.
3.2 배출가스 특성
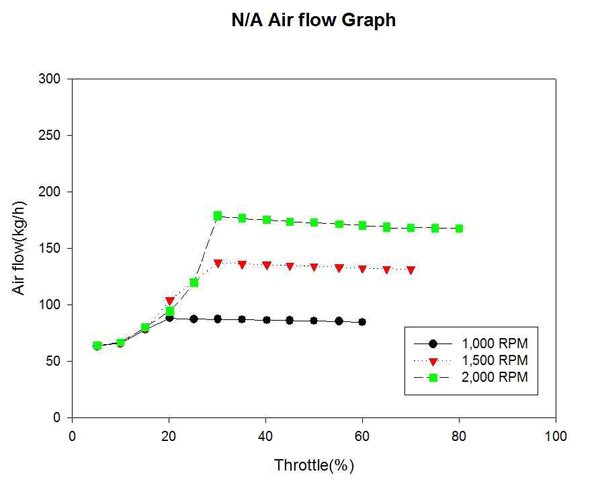
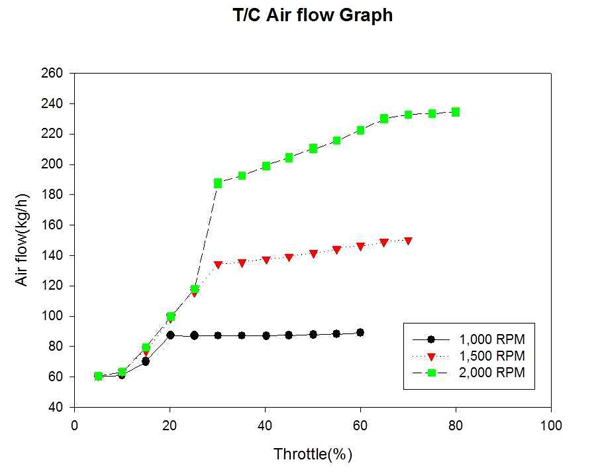
Figure 11은 자연흡기식 엔진의 각 고정 회전수까지의 공기유량 변화를 계측하여 비교한 것이다. Figure 12는 대응출력 220HP 과급기 장착에 따른 엔진의 각 고정 회전수까지의 공기 유량 변화를 계측하여 비교한 것이다. T/C 엔진이 효율을 나타내는 고속구간에서 공기유량은 자연흡기 엔진에 비해 급격히 증가 하였다. 이는 T/C에 의한 과급효과로 보인다.
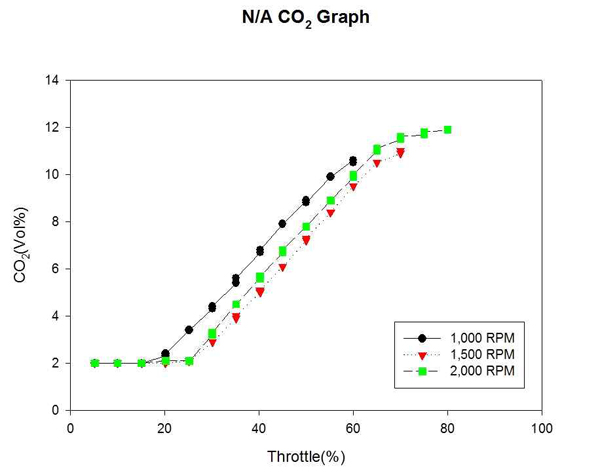
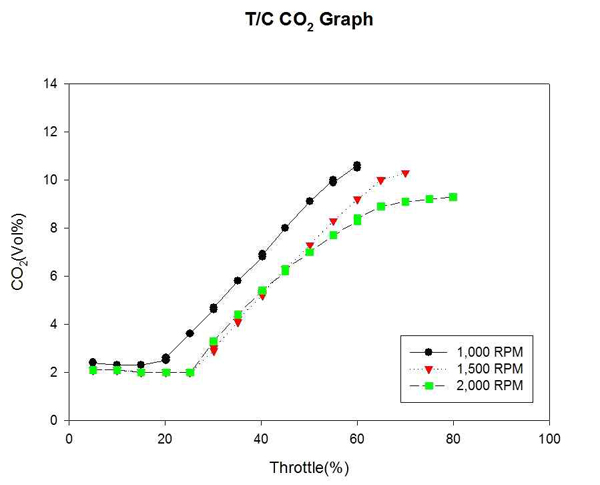
Figure 13은 자연흡기식 엔진의 각 고정 회전수까지의 CO2 변화를 계측하여 비교한 것이다. Figure 14는 대응출력 220HP 과급기 장착에 따른 엔진의 각 고정 회전수까지의 CO2 변화를 계측하여 비교한 것이다. T/C 엔진이 효율을 나타내는 고속구간에서 CO2 배출량이 급격히 감소하였다. 이는 Exhaust gas recirculation을 통해 배기가스가 환원되어 CO2배출이 감소된 것으로 예측된다.
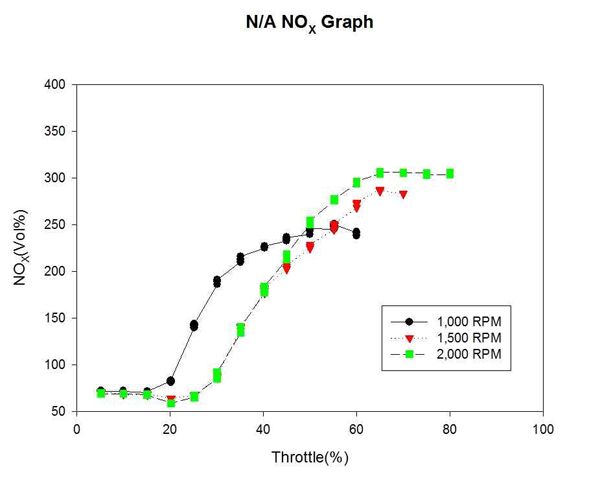
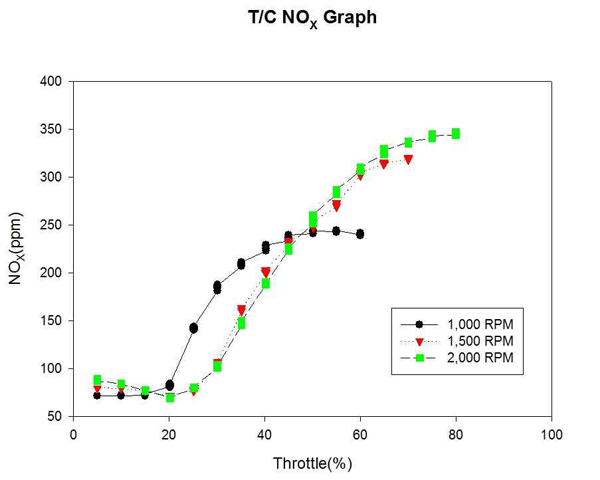
Figure 15는 자연흡기식 엔진의 각 고정 회전수까지의 NOX 변화를 계측하여 비교한 것이다. Figure 16은 대응출력 220HP 과급기 장착에 따른 엔진의 각 고정 회전수까지의 NOX 변화를 계측하여 비교한 것이다. T/C 엔진의 과급으로 인해 공기유량이 증가된 만큼 NOX의 배출량도 증가되었다. 이 역시 T/C 엔진이 효율을 나타내는 고속구간에서 급격히 증대되었으며, 저속구간에서는 큰 차이를 보이지 않았다.
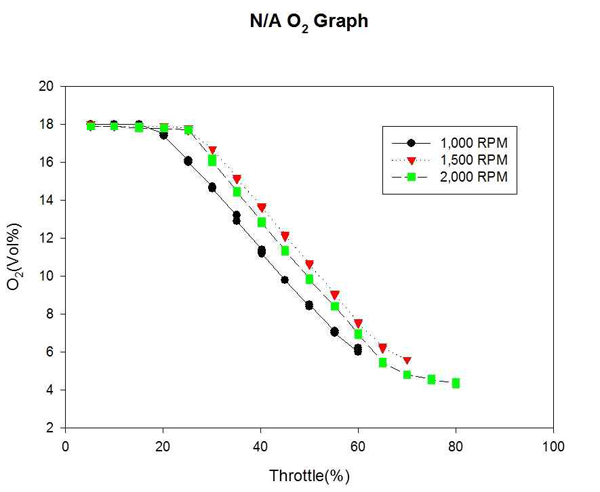
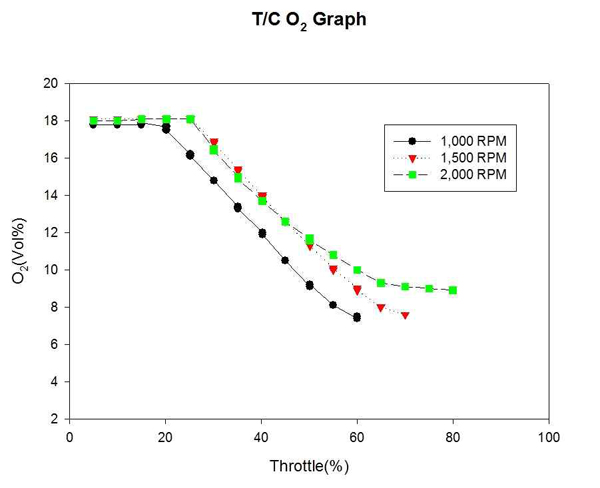
Figure 17은 자연흡기식 엔진의 각 고정 회전수까지의 O2 변화를 계측하여 비교한 것이다. Fig.18은 대응출력 220HP 과급기 장착에 따른 엔진의 각 고정 회전수까지의 O2 변화를 계측하여 비교한 것이다. 엔진에서 연소되는 O2에 비해 T/C 엔진이 과급 효율을 보이는 고속구간에서 과급되는 공기유량이 큰 만큼 고속구간에서 배출되는 O2의 배출량이 증가되었으며, 저속구간에서는 큰 차이를 보이지 않았다.
4. 결 론
본 연구에서는 자연흡기식 디젤엔진과 대응출력 220HP과급기가 장착된 디젤엔진을 대상으로 동일한 실험조건을 통해 엔진의 성능과 배출특성을 분석한 결과, 다음과 같은 결론을 얻을 수 있었다.
1) 엔진의 출력은 저속구간에서는 큰 차이를 보이지 않았으나 고속구간에서는 T/C를 적용함에 따라 13%가량 증가하였다.이는 일반적인 T/C엔진의 출력 효율이라 예측된다.
2) T/C엔진이 효율을 나타내는 고속구간에서 CO2배출량이 급격히 감소하였다. 이는 배기가스의 재순환을 통해 배기가스가 환원되어 CO2배출이 감소된 것으로 예측된다.
3) T/C엔진의 과급으로 인해 공기유량이 증가된 만큼 NOX의 배출량도 증가되었다. 이 역시 T/C엔진이 효율을 나타내는 고속구간에서 급격히 증대되었으며, 저속구간에서는 큰 차이를 보이지 않았다.
4) 실험 결과, T/C엔진의 동력 특성 및 배출특성으로 미루어 대응출력 220HPT/C엔진의 활용가치가 충분한 것으로 예측되며, 대응출력이 높은 T/C의 효율성을 뒷받침 해주는 결과라 예측된다.
References
- J. K. Yoon, “A study on the characteristics of performance and emission in a turbocharged D.I. diesel engine”, The Korean Society of Automotive Engineers, 1(1), p315-321, (2008), (in Korean).
- D. H. Seog, “A study on the performance improvement in a V8 type turbocharged intercooler D.I. diesel engine”, The Korean Society of Automotive Engineers, 13(2), p118-127, (2004), (in Korean).
- Y. C. Han, “A simulation study of diesel engine with turbocharger and intercooler”, The Korean Society of Machine Tool Engineers, 9(4), p123-130, (2000), (in Korean).
- N. J. Choi, “A study on the dynamic characteristics of a turbocharged diesel engine”, The Korean Society of Automotive Engineers, 3(1), p143-154, (1995), (in Korean).
- C. W. Lee, “A study on engine performance and exhaust emission characteristics of response power 150HP turbocharged diesel engine”, The Korean Society of Manufacturing Process Engineers, 11(6), p100-106, (2012), (in Korean).