Analysis of energy savings through an acknowledgement policy for efficient power management in LoRaWAN for IoT in a ship
Copyright © The Korean Society of Marine Engineering
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0), which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Abstract
As data-based ship management and control are required, Internet of Things (IoT) technology is increasingly needed to obtain and accurately transmit various types of information within ships. Considering an IoT network onboard a ship, technology that reduces the energy consumption of deployed wireless devices and guarantees reliable communication is essential for continuously acquiring various types of data within the ship and ensuring accurate data collection. The long-range wide-area network (LoRaWAN) protocol is a promising technology for IoT because it supports long-range communication and bit rates suitable for IoT applications. Applying the LoRaWAN protocol to IoT networking onboard ships requires energy-efficient operations. Although the LoRaWAN protocol generally has an energy-efficient operation, the low-complexity communication scheme, such as the deferred transmission of the downlink frame, limits the energy-efficient operation of the end devices. Therefore, this study proposes an energy-efficient scheme with an acknowledgement policy that complies with the LoRaWAN standard and analyzes the energy savings of the proposed method.
Keywords:
Long-range wide area network (LoRaWAN), Acknowledgement policy, Internet of Things (IoT)1. Introduction
As Internet of Things (IoT) technologies are being developed, their use and market size expand in various fields. To ensure stable and sustainable communication between wireless devices, several methods have been studied to increase the lifetime of each node by improving power consumption performance [1]. IoT nodes with communication and sensing capabilities require large communication ranges and limited battery power [2].
Recently, the demand for data-based ship management to en-hance the efficiency and safety of ships has increased, and net-working solutions that meet the requirements of the special envi-ronments of ships are required. For example, Voyage Data Re-corders (VDRs) must be installed on passenger and nonpassen-ger ships of 3,000 gross tons or more built after July 1,2002, to assist in accident investigations [3]. The VDR is a data recording system that collects onboard data using sensors distributed throughout the ship and is designed to comply with IMO's Inter-national Convention for the Safety of Life at Sea (SOLAS) re-quirements (IMO Res. A. 861 (20)) [4].
Ship IoT networks require technology that allows distributed IoT devices to maintain stable connections with low power con-sumption to collect various types of data accurately and continu-ously within the ship. The Long-Range Wide Area Network (LoRaWAN) [5]-[6] is a promising commercialized IoT technol-ogy because it supports low power consumption and bit rates suitable for long-range applications [2].
In a previous study [7], the energy waste problems of the Lo-RaWAN standard as an IoT solution for the data-centric man-agement of ships were analyzed, and improvement strategies were briefly proposed.
The remainder of this study is organized as follows: Section 2 explains the LoRaWAN data frame exchanges defined in the corresponding specification. In Section 3, we present a method for applying an energy-efficient acknowledgment policy to the LoRaWAN protocol. In Sections 4 and 5, the energy consump-tion of the LoRaWAN is analyzed and evaluated. Finally, con-cluding remarks are presented in Section 6.
2. LoRaWAN Data Exchange
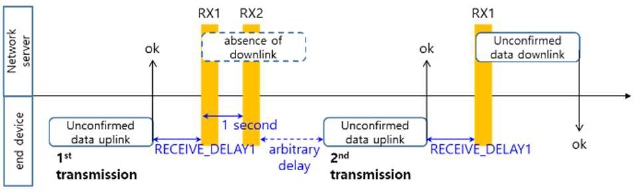
After a certain period of time has elapsed since the uplink transmission of the end device, one or two reception windows (RX1 and RX2) are opened to receive downlink frames from the network server [5]. Another uplink packet cannot be transmitted unless one of the following two conditions is met [5]: 1) the downlink packet from the network server is received in the RX1 or RX2 window associated with the previous uplink transmis-sion; or 2) the RX2 window associated with the previous uplink transmission expires.
An example of an unconfirmed data-frame exchange is depict-ed in Figure 1, where NbTrans is the maximum allowed number of uplink transmissions. As shown in Figure 1, the first transmit-ted uplink frame of the end device was correctly received by the network server. This figure shows that no downlink transmission occurred in the associated RX1 and RX2 windows [7]. If no downlink frame exists from the network server, the end device must wait for a random delay after the RX2 window is closed.
Because LoRaWAN end devices are power-limited, energy-efficient operation must be guaranteed. In the example shown in Figure 1, if the network server successfully receives the uplink frame and does not transmit the downlink frame to the end de-vice, more energy is wasted because of the additional transmis-sion and reception operations of the power-limited end device. Therefore, Section 3 proposes an alternative scheme using the LoRaWAN MAC command that supports energy-efficient opera-tions and complies with the LoRaWAN standard.
3. Proposed Scheme using LoRaWAN MAC Command
Automatic repeat request (ARQ) is an error control method for data transmission that uses acknowledgments to achieve reliable data transmission through unreliable communication channels. The acknowledgment policy operates in various ways depending on the communication protocol, and each policy has its own ad-vantages and disadvantages. Because the Immediate-ACK policy transmits an acknowledgement every time a MAC frame is transmitted, the overhead of the acknowledgement transmission is large. The No-ACK policy does not use acknowledgments in the MAC layer. Therefore, no transmission occurs overhead, but the throughput is lowered.
In the example shown in Figure 1, the No-ACK policy was applied. Thus, if the network server successfully receives an uplink frame and no downlink frame is to be transmitted to the end device, energy is wasted because of the additional transmis-sion and reception operations of the end device. This type of energy loss can be prevented if the downlink frame is transmitted immediately from a network server.
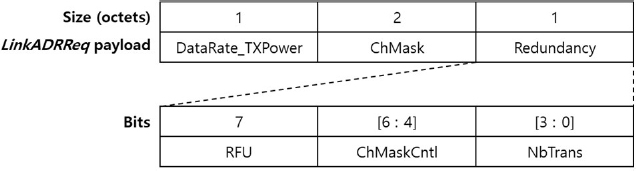
To propose an alternative that complies with the LoRaWAN standard, the LinkADRReq MAC command defined in the current LoRaWAN standard is illustrated in Figure 2. A network server may use the LinkADRReq MAC command to request that an end device perform rate adaptation and set the maximum transmission power. This MAC command has a 1-octet Redundancy field, which consists of the reserved for future use (RFU), channel mask control (ChMaskCntl), and NbTrans fields, as shown in Figure 2.
This study proposes a method for utilizing the RFU field (bit-7) to prevent unnecessary additional transmission and reception of the end device, as shown in the example in Figure 1. For this purpose, the network server sets the corresponding bit to 1 and transmits the MAC command. In addition, if the RFU field is 1, the terminal does not need to send LinkADRAns, thus preventing uplink transmission owing to this MAC command.
4. Analysis of Energy Consumption
When the acknowledgment policy is changed to Immediate-ACK by applying the method proposed in Section 3 using LinkADRReq, the average power consumption E[Pimm-ACK] is as follows:
| (1) |
where Ptx, Prx, and Pdetect are the powers consumed for packet transmission, reception, and preamble detection, respectively. PIDLE represents the power consumption in the IDLE state. Ttx and Trx represent the uplink and downlink dwell times, respec-tively. Prx is defined in Equation (2), depending on whether a downlink data frame is present.
| (2) |
5. Numerical Result
Based on the number of uplink packet transmissions (n), the ratio of energy consumption for each element (Ptx, PIDLE, 1, PIDLE, 2, Pdetect, and Prx) of the proposed scheme compared with the conventional LoRaWAN policy is shown in Figure 3. In this analysis, it was assumed that the Prx of LinkADRReq in Equation (2) is 50% of the downlink data frame reception power con-sumption. As the number of transmissions increased, the energy consumption of the proposed method decreased rapidly. In addi-tion, the PIDLE, 2 and Pdetect components were not consumed, and Prx was reduced by the ratio of the LinkADRReq reception power to the downlink data frame reception power.
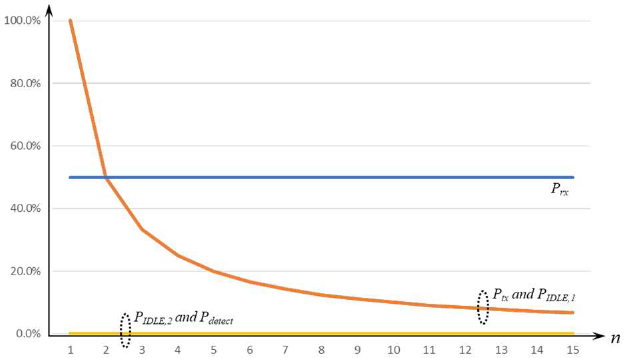
Energy consumption ratio of the proposed method to the conventional method with respect to each power element
As shown in Figure 3, the Immediate-ACK policy using the LinkADRReq MAC command improved the energy efficiency of the LoRaWAN by reducing the overall energy consumption. Therefore, to reduce the unnecessary energy consumption of the end device, a network server with stable power must immediately transmit downlink frames, such as the LinkADRReq MAC command.
6. Conclusion
This study analyzed the energy consumption of the proposed acknowledgement scheme for the LoRaWAN protocol. The pro-posed Immediate-ACK policy using the LinkADRReq MAC command improved the energy efficiency of the LoRaWAN end device by reducing overall energy consumption. Because the proposed alternative complies with LoRaWAN standards, it can be easily applied to commercial LoRaWAN systems.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y. -I. Joo; Methodology, Y. -I. Joo; Writing-Original Draft Preparation, Y. -I. Joo; Validation, Y. -I. Joo; Writing-Review & Editing, Y. -I. Joo.
References
- J. de Carvalho Silva, J. J. P. C. Rodrigues, A. M. Alberti, P. Solic, and A. L. L. Aquino, “LoRaWAN — A low power WAN protocol for Internet of Things: A review and oppor-tunities,” in Proceeding of 2017 2nd International Multidis-ciplinary Conference on Computer and Energy Science (SpliTech), pp. 1-6, 2017.
-
Y. -I. Joo, “Networking strategy for data-driven manage-ment in a ship: Requirements and applications,” Journal of Advanced Marine Engineering and Technology, vol. 46, no. 4, pp. 193-195, 2022.
[https://doi.org/10.5916/jamet.2022.46.4.193]
- Voyage Data Recorders, https://www.imo.org/en/OurWork/Safety/Pages/VDR.aspx, , Accessed May 11, 2022.
- Voyage Data Recorders, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Voyage_data_recorder, , Ac-cessed May 11, 2022.
- LoRa Alliance, LoRaWAN L2 1.0.4 Specification, TS001-1.0.4, October, 2020.
- SEMTECH, LoRa and LoRaWAN: A technical overview, Semtech Corporation, December, 2019.
- Y. -I. Joo, “Analysis of energy savings through acknowl-edgement policy for efficient power management in Lo-RaWAN for IoT in a ship,” Journal of Advanced Marine Engineering and Technology, vol. 46, no. 4, pp. 193-195, 2023.